CT – Computed tomography
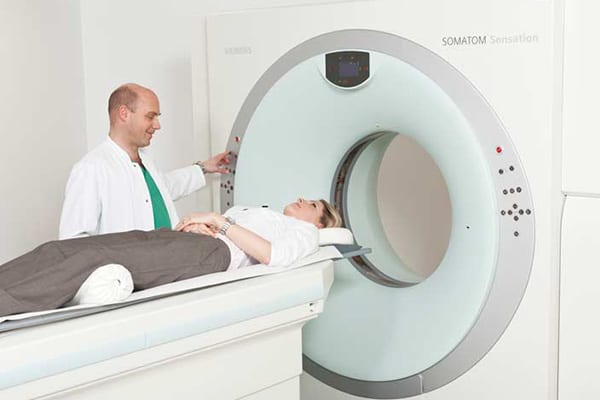
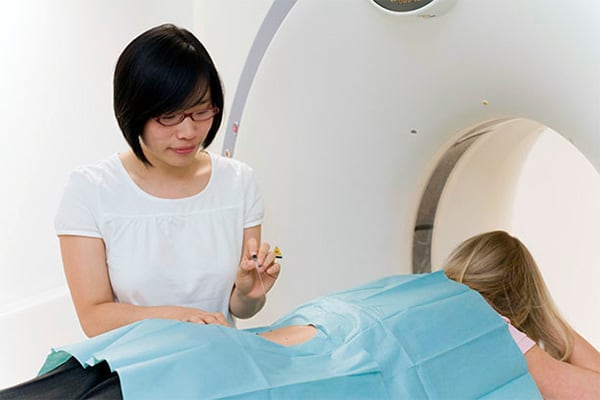
The CT of the Beta Klinik
Beta Klinik features a multi-spiral CT. The advantage of this particular CT is a combination of pace, high-definition image quality and reduced radiation. These key aspects make it first choice for clinical examinations and research. Since patients vary in terms of height, weight and anatomy, the radiation exposure is adapted to each individual in order to save radiation up to 68%.
Since our CT employs the multislice spiral technique, X-ray tubes and detectors rotate around the body in a fast pace enabling comprehensive examination in short time. This short examination time is especially suitable to elderly patients and patients who are only able to lay down very shortly. Even examinations making breath control necessary are feasible and bearable not only for patients with a short breathe. Additionally, image artifacts are reduced, which is very important for heart examinations.